Treating wounds with Keroderm®
Keroderm® is suitable for the treatment of small, superficial wounds. Bacteria-inhibiting, nurturing and tissue-forming active ingredients support the skin’s natural ability to regenerate. The ointment is also characterised by extremely good protective film formation and excellent moisturising properties.
Cuts
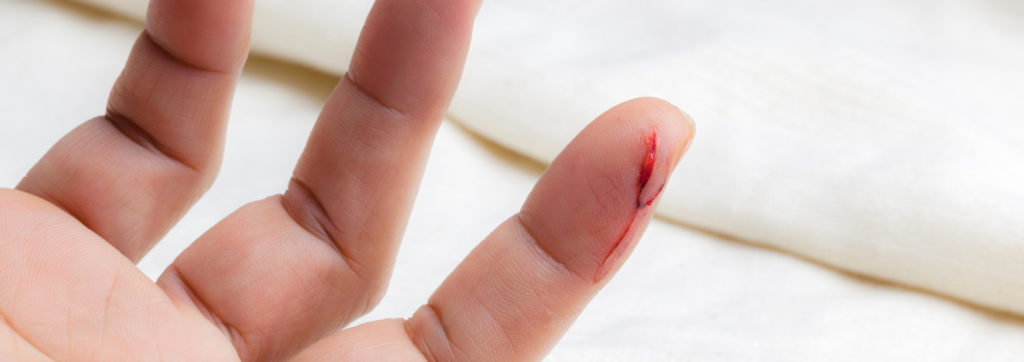
Cuts are mainly caused by sharp objects. The most common cuts are caused by broken glass, tools, paper, razor blades, knives and kitchen utensils.
Cuts that are not particularly deep primarily injure the uppermost layers of the skin. If a blood vessel under the epidermis is injured, there will be a lot of bleeding. In general, minor cuts are not dangerous. Although bleeding is unpleasant and appears threatening, it serves to clean the wound in a natural way and to prevent any infection caused by bacteria that may have penetrated the skin.
In the case of very deep wounds, a doctor should be consulted and the wound should be stitched.
Scratch wounds
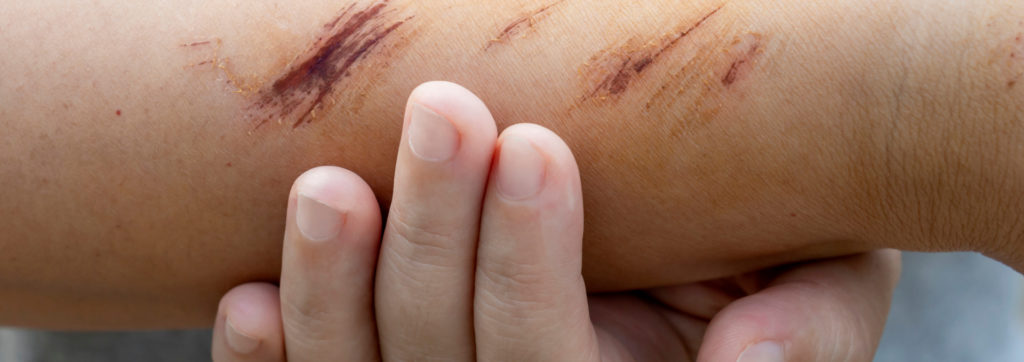
Scratch wounds are usually caused by thorns and spines of plants, claws or fingernails and are similar to lacerations or cuts. Itchiness that leads to frequent scratching can also cause scratch wounds. The pressure on the tissue causes the skin to tear superficially and the wound can vary in size, depending on the cause.
Scratch wounds are often superficial wounds that bleed only slightly to moderately but cause slight pain or an unpleasant burning sensation. As the injured blood vessels contract, the blood begins to clot and a crust forms.
Abrasions
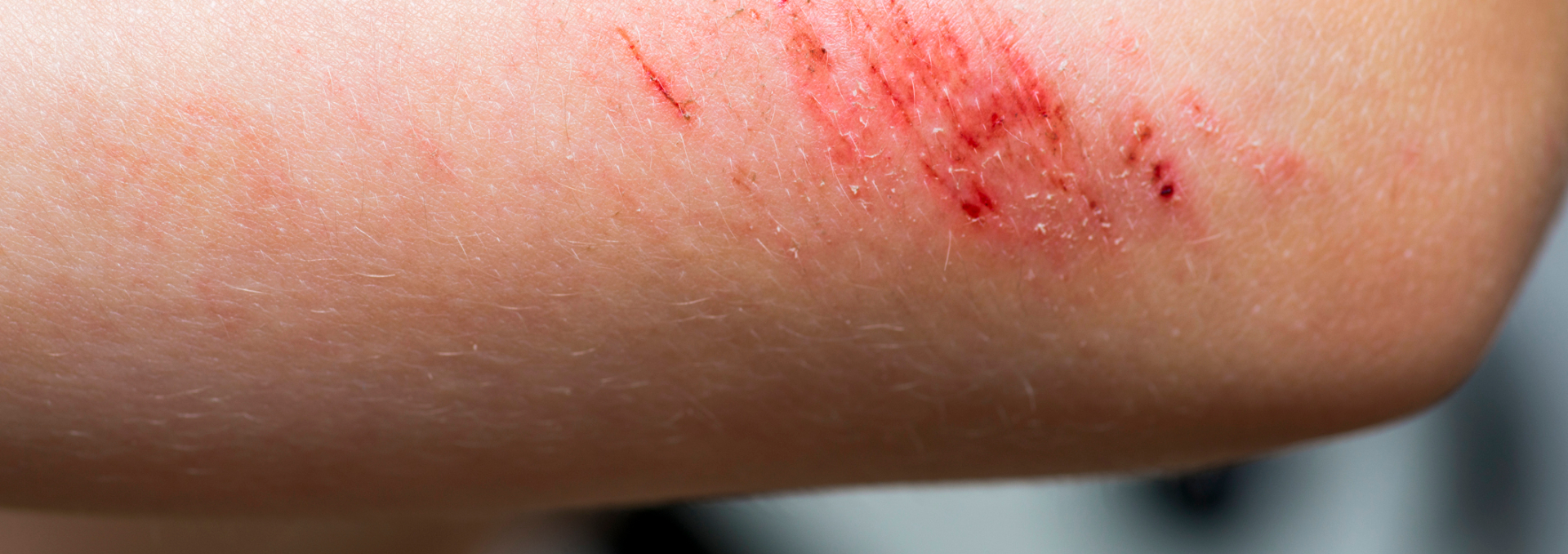

Abrasions are among the most common everyday injuries. Children and adolescents are particularly affected, as they can easily get abrasions from rubbing over rough surfaces while playing or doing outdoor sports. Knees, palms, elbows and faces are particularly often affected.
Abrasions are wounds in which only the top layer of skin (epidermis) is damaged. Since there are no blood vessels in this layer of skin, the abrasion does not bleed. If bleeding does occur, it means that the dermis underneath the epidermis has been injured, which can lead to an infection. For this reason, abrasions should always be treated. Generally, abrasions heal quickly and rarely leave scars.
Fissures

The elasticity of the skin can be reduced by cold temperature, dry air or prolonged rubbing/pressure. Especially on the hands and feet, the tissue can break open and cracks or furrows appear in the skin – so-called fissures. These unsightly fissures affect not only the aesthetic appearance of the skin, but also the natural barrier function of the epidermis. This damage promotes the penetration of harmful substances into the lower layers of the skin and can lead to infections, which can itch, burn or even bleed. In the case of inflammation, it is imperative to seek medical treatment.
Blisters
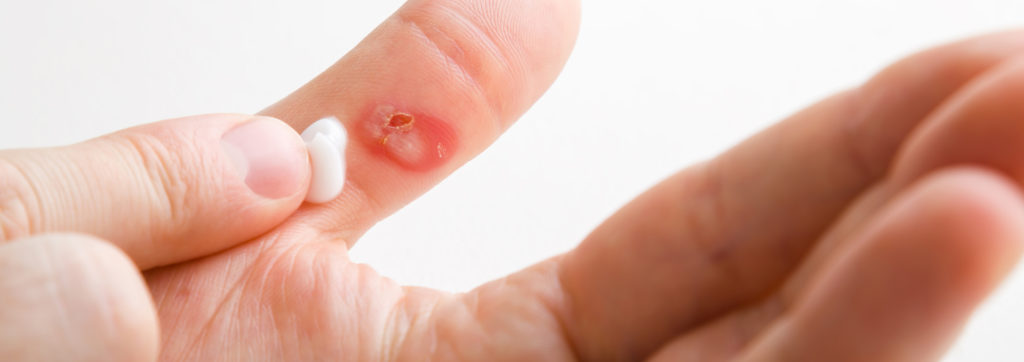
Blisters are often caused by new shoes or by the unaccustomed use of a tool. They usually occur on the feet or hands. Whenever a part of the skin is subjected to a lot of friction and the upper layer of skin pushes against the lower layer of skin, a cavity is created in between that fills with tissue water.
If you feel a blister it is usually already too late, and the resulting burning pain makes it impossible to continue the activity that caused it. It is only when a callus develops in the affected areas that further blisters are prevented from forming.
Since open blisters run the risk of coming into contact with germs, it is essential to disinfect them first before treating them with a regeneration ointment.